What is Python?

Python is an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics. Its high-level built in data structures, combined with dynamic typing and dynamic binding, make it very attractive for Rapid Application Development, as well as for use as a scripting or glue language to connect existing components together. Python's simple, easy to learn syntax emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. Python supports modules and packages, which encourages program modularity and code reuse. The Python interpreter and the extensive standard library are available in source or binary form without charge for all major platforms, and can be freely distributed.
Developer: Python Software Foundation
First appeared: 20 February 1991; 33 year
Uses of Python:

Web development
Game development
Business
Data and information visualization
Desktop GUI
Software development
Web scraping applications
Operating Systems
Education
Open source
Python web development
Science
Software Testing
Blockchain
Desktop applications
Embedded system
Finance
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Scripting
Data science
Data analytics
Machine learning
Automation
Everyday tasks
Advantages of Python:
Easy to Learn and Use.
Free and Open-Source.
Rapid Development.
Interpreted Language.
Wide Range of Libraries and Frameworks.
Dynamically Typed.
Portability.
Strong Community Support.
Basic codes of Python:
Hello World:

Variables and Data Types:

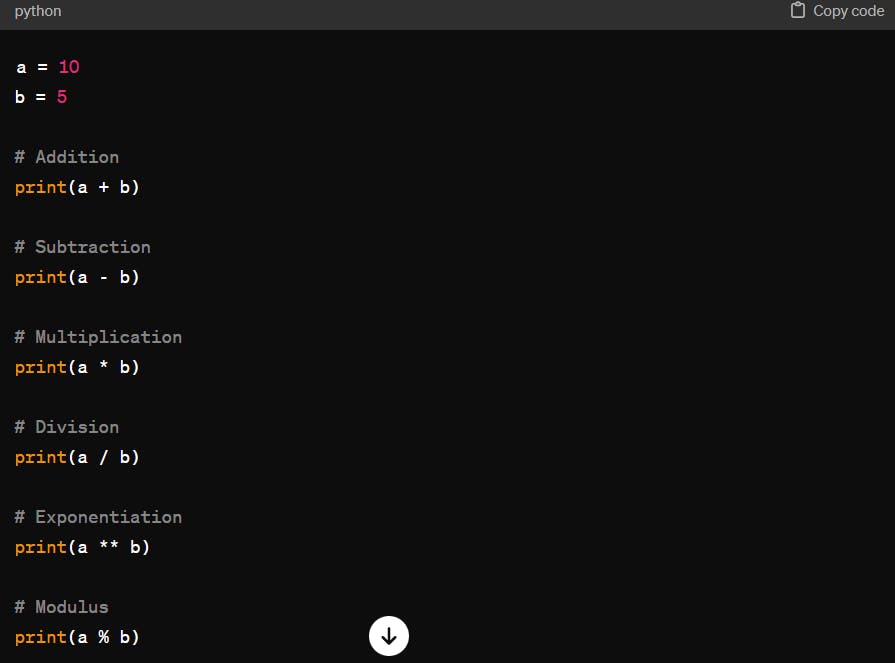
Arithmetic Operations*:*
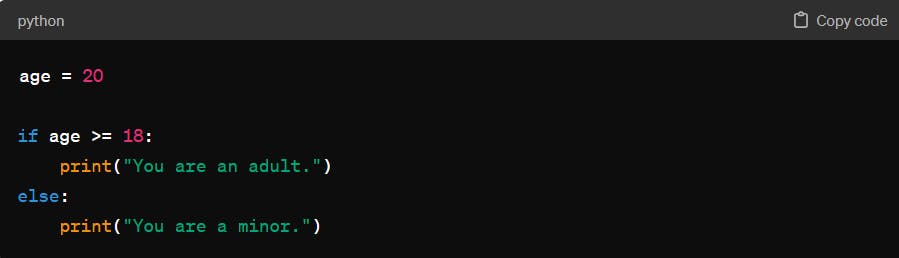
Conditional Statements*:*
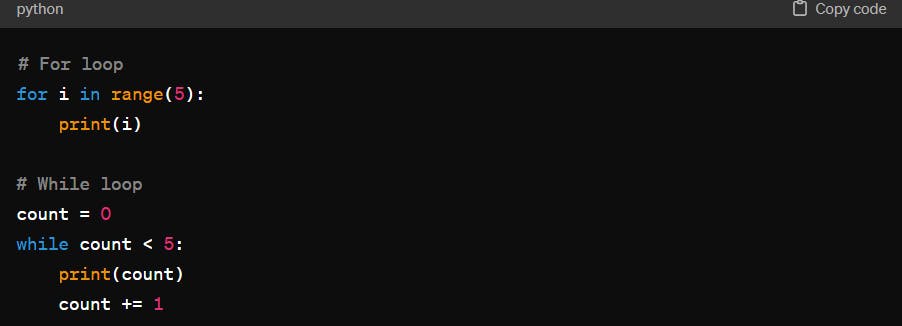
Loops:
Conclusion: Python is a versatile and beginner-friendly programming language that is well-suited for a wide range of applications. Its readability, simplicity, and extensive standard library make it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced developers alike.